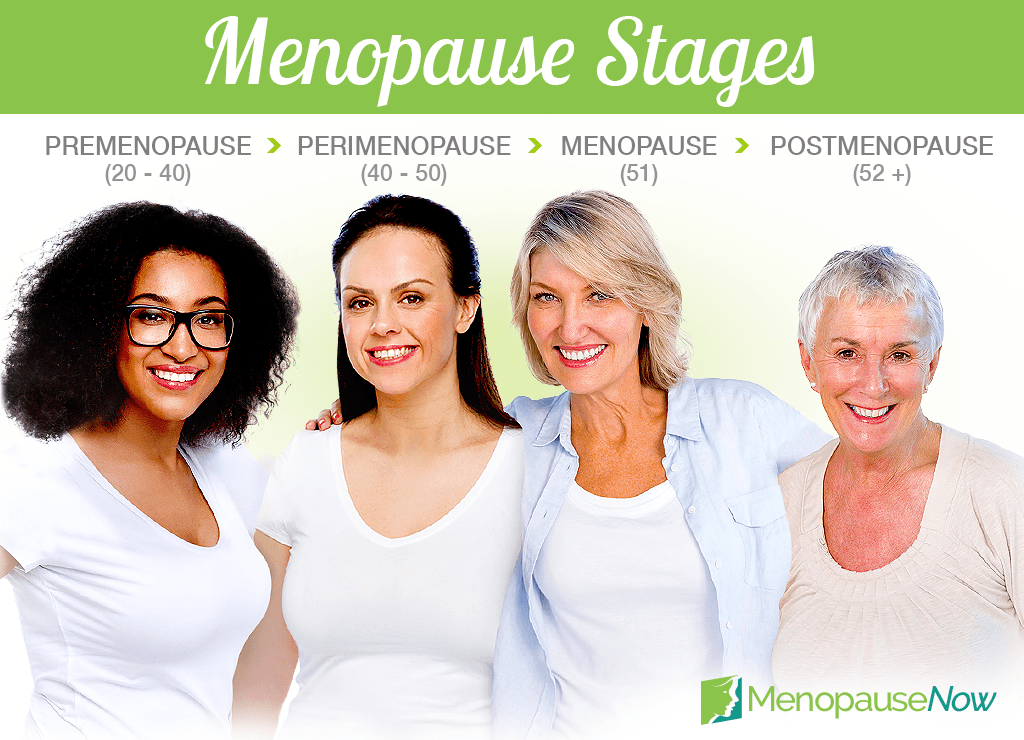
Menopause Stages
Premenopause
What Is It?
Premenopause is the first stage in a woman's reproductive life, during which she has the highest chances of getting pregnant.
When Does it Start and End?
Premenopause begins at puberty and lasts until she enters the menopausal transition in her early to mid-40s.
What Happens in Premenopause?
In premenopause, female fertility is at its best, although it gradually declines with age, especially once women enter their mid-30s. There are no menopause symptoms in this stage, but women might experience occasional discomforts from hormonal fluctuations around the time of their periods, such as premenstrual syndrome (PMS), or ovulation.
Perimenopause
What Is It?
Perimenopause is the beginning of the menopausal transition, or - as its own name signifies - the time “near menopause.”
When Does it Start and End?
It can begin in a woman's early to mid-40s and last for 2 to 10 years until a woman enters menopause.
What Happens in Perimenopause?
During perimenopause, drastic fluctuations of key reproductive hormones, estrogen and progesterone, trigger infamous menopause symptoms, like irregular periods, night sweats, or mood swings, causing women to feel uncertain about their own bodies as they go toward the end of their reproductive years.
Menopause
Menopause is defined as a point in time when menstrual cycles have not occurred for 12 consecutive months, marking the end of a woman's reproductive years.
Menopause occurs due to aging as the ovarian egg supply naturally depletes, ceasing the production of reproductive hormones. As a result, a woman stops menstruating and can no longer get pregnant. The average age of menopause is 51, but women can enter it between the ages of 45 and 55.
Postmenopause
What Is It?
Postmenopause is the final reproductive stage, covering the years after menopause.
When Does it Start and End?
Women enter postmenopause a year after they have missed their monthly periods, which typically occurs in their early 50s and lasts for the remainder of their lives.
What Happens in Postmenopause?
During postmenopause, the majority of bothersome menopause symptoms naturally lessen or cease, although some women continue struggling with vaginal dryness, insomnia, and urinary tract infections. Moreover, persistently low estrogen levels put postmenopausal women at a higher risk for developing potentially dangerous health conditions, including heart disease or osteoporosis.
Others
Early Menopause
What Is It?
Early menopause occurs when a woman's periods permanently stop between the ages of 45 and 50. It affects up to 5% of women.
Why Does it Occur?
Early menopause might occur due to an untimely loss of ovarian function, which can be triggered by genetics, certain autoimmune diseases, or medical interventions.
What are the Effects of Early Menopause?
Women undergoing early menopause experience similar symptoms to those in natural menopause, but – in some cases – they might be more severe. They are also at a greater risk for developing health conditions related to constantly low estrogen levels, including osteoporosis or heart disease.
Premature Menopause
What Is It?
Premature menopause is a term used to describe menopause that happens before the age of 40. It is rare as it only affects about 1% of women in their 40s.
Why Does It Occur?
Premature menopause can occur naturally because of primary ovarian insufficiency or can be induced medically through radiation, chemotherapy, or surgery.
What are the Effects of Premature Menopause?
Women who have undergone premature menopause cannot get pregnant naturally, though pregnancy is possible with donor eggs through IVF. Also, because women spend a bigger portion of their lives without the protective effects of estrogen, they are at a higher risk for strokes and osteoporosis.