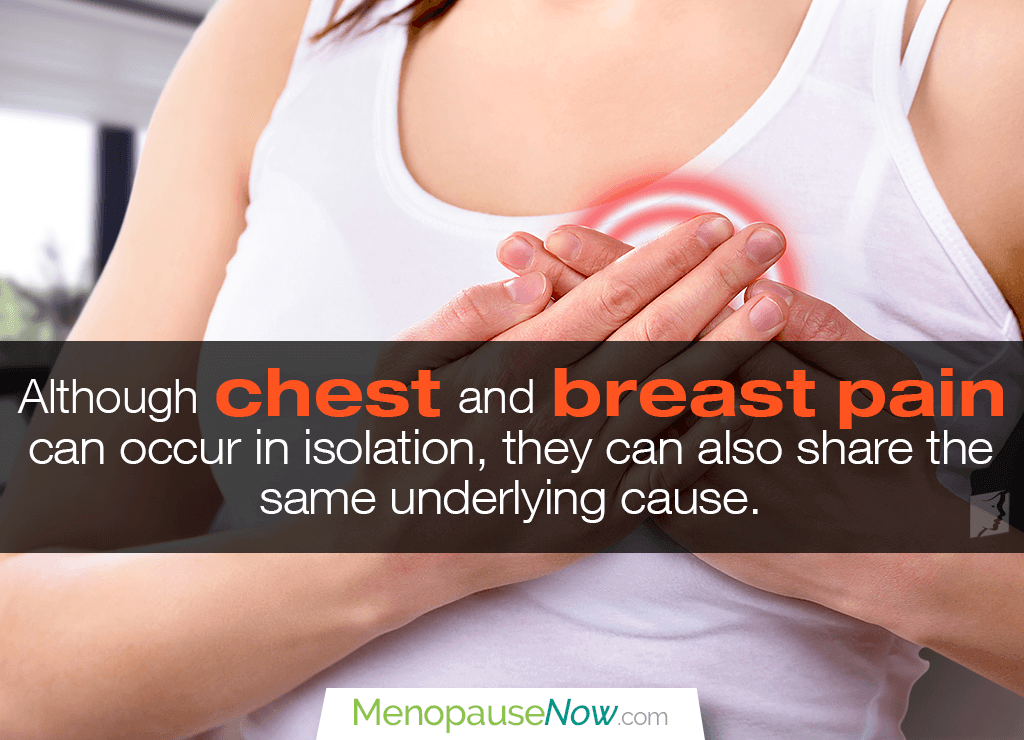
Chest and breast pain can be a source of concern, especially when unable to pinpoint the cause. Although the two conditions can occur in isolation, they can also be related to one another. Continue reading to discover the most important things to know about chest and breast pain for better knowledge and optimal health.
About Chest and Breast Pain
While many believe chest pain to be indicative of heart problems, it can actually originate from any organ or tissue in the chest - such as the lungs, esophagus, ribs, and muscles - and radiate to the breasts, provoking discomfort in the both.
On the other hand, breast pain is much more common than chest pain and affects almost half of all women at some point during their lives.1 Severity can vary from a mild ache to an intense sharp or throbbing pain.
Symptoms of both chest and breast pain can be:
- A feeling of pressure, fullness, or tightness in the chest
- Pain that moves to the back, neck, jaw, shoulders, and arms
- A pain that increases with deep breathing or coughing
- A feeling of tenderness or soreness when the chest or breast is pushed or touched
- Pain felt in the upper, outer area of breasts, possibly extending to the armpits and arms
The severity and duration of the symptoms depends greatly upon the underlying cause.
Causes
As aforementioned, certain chest pain conditions can feel as if they're coming from the breasts, yet that is not so as just their pain is radiating to the breasts.
As such, health problems that can result in chest and breast pain include, but are not limited to:
- Sore muscles. Chronic pain syndromes - like fibromyalgia - can create muscle-related pain in the chest and breast.
- Muscle strain. Pulling the pectoralis major muscle can emit pain from the chest to the breast. Activities that can strain this muscle include shoveling, lifting, or raking.
- Arthritis. Arthritis in the neck or upper back can trigger chest and breast pain as it may distress nerves from the upper spinal cord.
- Angina. Angina is poor blood flow to the heart that is often due to a thick buildup of plaque on the inner walls of arteries. It can result in a heart attack if not taken care of properly.
- Heartburn. Often due to acid reflux, this happens as a result of stomach acid washing up to the esophagus. It can occasionally cause chest and breast pain.
- Costochondritis. Costochondritis is an inflammation of the rib cartilage that is sometimes called chest well pain, costosternal syndrome, or costosternal chondrodynia.
Relief for Chest and Breast Pain
Some measures may be recommended for a healthy start toward comfort, including:
- Avoiding strenuous activities
- Applying an ice pack to the area throughout the day
- Taking over-the-counter pain medications
Nevertheless, effectively treating chest and breast pain will depend on what is causing the discomfort. Speak with your doctor to develop a treatment plan for your specific case.
When Should I Worry?
Breast pain is not normally a cause for concern. So, if it is occurring in isolation, then it in unlikely to be a result of anything serious, especially if occurring during menopause.
However, sudden chest pain that lasts longer than a few minutes; started with shortness of breath, feeling sick, and perspiration; spreads to the arms, back, neck, or jaw; and makes the chest feel heavy and tight should be immediately treated.
Conclusions
It is essential for women to remember that they are in control of their overall health. Any condition causing chest and breast pain needs to be addressed before the discomfort subsides. This may involve a little investigative work and patience.
For women whose chest and breast pain is indicative of hormonal changes, natural and effective menopause symptoms treatments can help them find ultimate comfort far into their twilight years.
Sources
- Harvard Health Publications. (2018). Breast pain: Not just a premenopausal complaint. Retrieved November 13, 2019, from https://www.health.harvard.edu/pain/breast-pain-not-just-a-premenopausal-complaint
- Mayo Clinic. (2017). Chest pain: Symptoms & causes. Retrieved November 13, 2019, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/chest-pain/symptoms-causes/syc-20370838
- MedlinePlus. (2018). Chest pain. Retrieved November 13, 2019, from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003079.htm
- National Breast Cancer Foundation. (n.d.). Breast Pain. Retrieved November 13, 2019, from http://www.nationalbreastcancer.org/breast-pain
- NHS. (2017). Chest pain | Breast pain. Retrieved November 13, 2019, from http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/chest-pain/Pages/Introduction.aspx | https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/breast-pain/
Footnotes:
- Cleveland Clinic. (2014). Breast Pain (Mastalgia). Retrieved November 13, 2019, from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15469-breast-pain-mastalgia