Women who suffer from unexplained bouts of water retention may feel frustrated for not knowing exactly what brought it about and how to tackle the symptom once and for all. Continue reading to learn all about water retention, from causes and symptoms to management, treatment, and much more.
About Water Retention
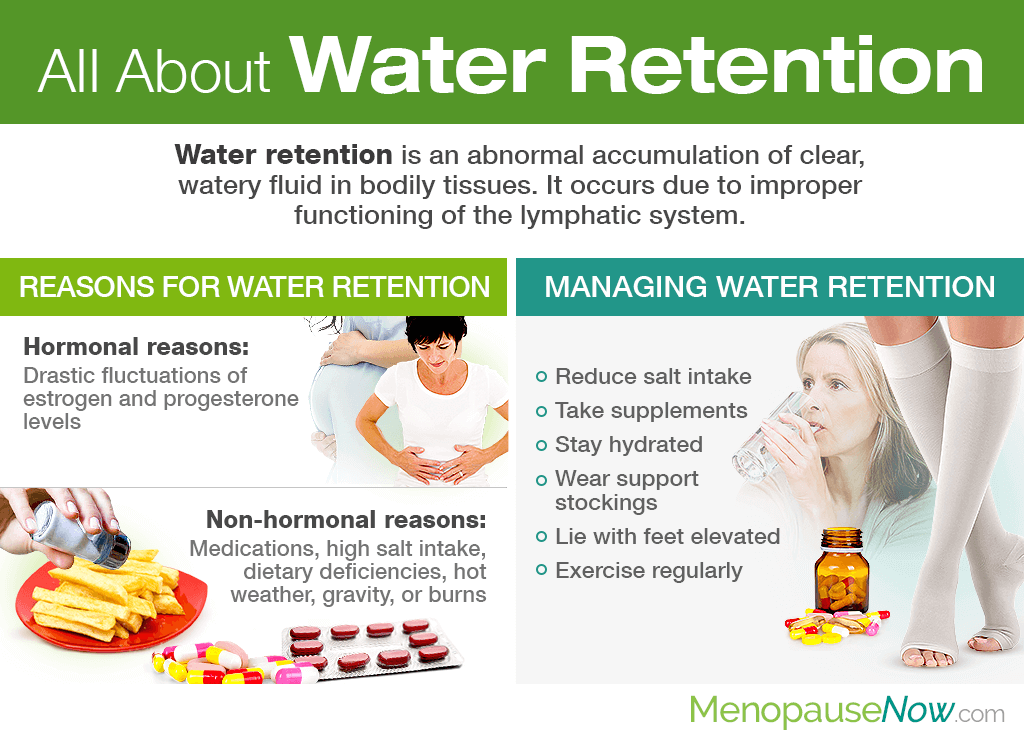
Water retention - also known as edema or fluid retention - is an abnormal accumulation of clear, watery fluid in bodily tissues.
It occurs due to improper functioning of the lymphatic system, which is a network of tubes that drain fluid from the tissues into the bloodstream. When the fluid is not drained properly, fluid retention occurs.
Reasons for Water Retention
There are various reasons for water retention in women of all ages, from hormonal to non-hormonal causes.
Hormonal Reasons

When women are in periods of hormonal flux, such as pregnancy or menopause, their bodies are more apt to retain water since reproductive hormones, specifically estrogen and progesterone, have crucial effects on body fluid regulation.
Until the hormones are regulated, women's bodies will continue retaining water, and it will not be easy to get rid of water weight.
Non-hormonal Reasons

Common, non-hormonal causes of water retention are due to medications, high salt intake, dietary deficiencies, hot weather, gravity, or burns.
Other underlying medical conditions that could cause fluid retention include chronic lung, thyroid, kidney, autoimmune, or liver diseases; allergic reactions; heart failure; arthritis; or cancerous tumors.
Symptoms of Water Retention
Symptoms of fluid retention include:
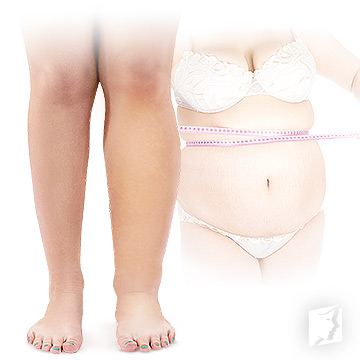
- Unexplained weight fluctuations
- Stiff joints
- Aching body parts
- Rapid weight gain over a few days or weeks
- Swelling of affected body parts (feet, ankles, hands, etc.)
- Pitting edema, which is when the skin may hold an indent for a few seconds when pressed
- Non-pitting edema, which is when the skin may not hold an indent when pressed
Diagnosing Water Retention
First, women will start with a medical history and physical exam by their doctors. Then, blood or urine tests will be ordered to measure reproductive hormone levels, especially in those passing through periods of reproductive significance, such as pregnancy or perimenopause. Other hormones deemed necessary to check may also be included.
If blood or urine tests come out with normal results, function tests will be ordered for the liver, kidney, or heart to test for the presence of an underlying medical condition that may be causing edema.
Managing Water Retention
Women who are suffering from mild bouts of fluid retention may do well with battling it the following ways:
Reduce salt intake. Refrain from salty, processed foods, such as potato chips and manufactured meats, and add minimal amounts of salt into homemade meals.
Take supplements. Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine), vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid), calcium, vitamin D, and magnesium are just a few nutrients renowned for helping in cases of slight fluid retention.
Stay hydrated. Well-hydrated bodies are less likely to retain fluid. Drink between six to eight glasses of water daily.
Wear support stockings. These compression socks create pressure on the legs to fight edema and improve blood flow.
Lie with feet elevated. Lie with your legs higher than your heart level to work against gravity, which pulls on body fluids and may encourage them to pool in lower limbs.
Exercise regularly. Any form of exercise will foster sweating, which is a healthy way to reduce water retention. Although, make sure to stay properly hydrated throughout the workout session.


Although management techniques will work short-term, long-term relief can be found by seeking an effective treatment plan.
Water Retention Treatment
It is important to determine the underlying cause of water retention before pursing treatment. Nevertheless, for menopausal women, this root cause is generally hormonal imbalance.
Water retention and bloating treatments stress lifestyle changes of an improved diet, regular exercises, and healthy habits alongside the use of alternative medicines, such as phytoestrogenic herbal supplements or hormone-regulating supplements, to bring women long-lasting relief from fluid retention.
These treatment options will not only reduce water retention, but they will also alleviate other menopause symptoms at the same time, bringing women overall well-being for years to come.
Sources
- Stachenfeld, N.S. (2014). Hormonal Changes During Menopause and the Impact on Fluid Regulation. Reproductive Sciences, 21(5), 555-561. doi: 10.1177/1933719113518992
- Victoria State Government. (2017). Fluid retention (oedema). Retrieved April 9, 2019, from https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/Fluid-retention-oedema