Mood swings, insomnia, fatigue, and depression: all just signs of menopause, right?
Not necessarily.
While it remains true that these symptoms can be early indications of perimenopause, these experiences might also suggest the onset of thyroid dysfunction. Unfortunately for those suffering from thyroid disease, the numerous similarities between the two phenomena mean it can be difficult to determine which one a woman is suffering from. The problem isn't aided by the fact that both thyroid disorders and menopause typically occur at around the same time. Risks arise when women, unknowingly suffering from thyroid disease, fail to seek medical advice, as they believe themselves to be just going through menopause.
What Are the Differences between Thyroid Disease and Menopause?
Thyroid disease and menopause's shared symptoms can make the two hard to distinguish from one another. However, there are several key differences that can provide vital clues.
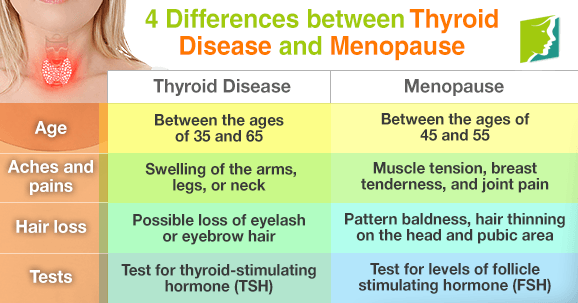
Age
Women most commonly experience menopause between the ages of 45 and 55, although some symptoms can occur earlier or later in life. However, thyroid conditions can be experienced over a much larger time scale: hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism are most commonly encountered between the ages of 35 and 65.
Aches and pains
While both menopause and thyroid diseases can led to multiple aches and pains, several distinctions can be made. Menopause is typically characterized by muscle tension, breast tenderness, and joint pain. Thyroid disease, on the other hand, generally manifests as swelling in the arms, legs, or neck.
Hair loss
One key characteristic of thyroid conditions is the potential loss of eyelash or eyebrow hair. Although hair loss may also occur during menopause, it generally manifests as female pattern baldness or hair thinning.
Diagnostic tests
If you are still uncertain about the cause of your symptoms, seeking medical advice is recommended, as doctors can conduct tests that provide a more definitive answer. To test for menopause, a doctor will examine levels of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). Separate tests to measure levels of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) will be conducted if the doctor suspects thyroid disease.
More Information about Menopause
Insomnia, mood swings, depression, and fatigue - all are common symptoms of menopause. Unfortunately, however, women might also experience some lesser known ones, too, such as electric shock sensations, digestive problems, memory lapses, and burning tongue.
Sources
- BMJ Group. "Menopause: What is it?" Patient Leaflet. 2007.
- Hopkins, Virginia. Lee, John R. M.D. What Your Doctor May Not Tell You About Menopause. New York: Warner Books Inc., 1996.
- Love, Susan M.D. Menopause and Hormone Book. New York: Three Rivers Press, 2003.
- Martin, Raquel. The Estrogen Alternative. Rochester, VT: Healing Arts Press, 2000.