Loss of libido during menopause can be caused by a wide array of factors. Like many menopause symptoms, loss of libido is primarily due to hormonal imbalance. However, physical, psychological, and relationship issues can negatively impact sex drive during menopause as well. Keep reading for an in-depth look at what causes loss of libido during menopause.
Hormonal Causes of Loss of Libido
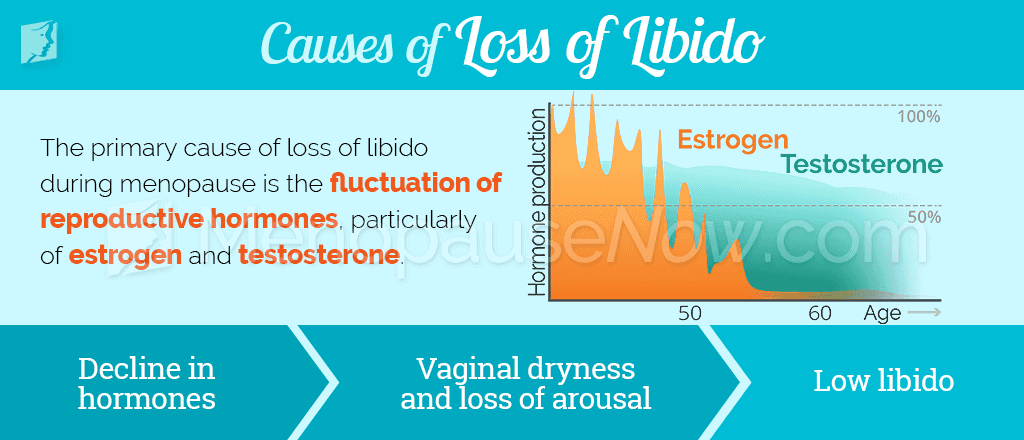
During menopause, one of the most prominent causes of loss of libido is hormonal imbalance. Decreased production of estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone can contribute to the reduction in sex drive and energy.
Estrogen
Estrogen plays a vital role in female sexuality by increasing sensations, assisting in the vaginal lubrication, and maintaining the health of vaginal tissue. As a woman approaches menopause, her body begins to produce less estrogen. This may trigger a myriad of symptoms that can contribute to loss of libido.
For example, drops in estrogen are primarily responsible for hot flashes, night sweats, irregular periods, and vaginal dryness, all of which can cause or contribute to loss of libido.
Testosterone
As with estrogen, the body begins to produce lower levels of testosterone with age. Experts believe that this drop in testosterone can also cause women to experience loss of libido around the time of menopause.
Progesterone
Progesterone is also integral to maintaining sexual health. When levels are too low during menopause, the resulting irregular periods, fatigue, and other menopause symptoms can cause loss of libido.
While hormonal change is often a major cause of loss of libido during menopause, other factors can also contribute to a woman's loss of libido. Read on to learn about the other potential causes of loss of libido.
Other Causes of Loss of Libido
Physical causes
A number of physical and health-related factors can trigger loss of libido during menopause. Women who experience unusual symptoms in addition to reduced sex drive should speak with their physicians to rule out any serious health conditions. Women with one or more of these conditions may find that pre-existing health conditions are responsible for their loss of libido.
HRT and Testosterone
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) or low-dosage birth control pills can affect testosterone production, leading to a loss of libido. If taken orally, these pills are metabolized in the liver, which then puts out a protein that binds to testosterone, inhibiting it and thus decreasing desire.
- Sexual dysfunction. Loss of libido can often be due to sexual dysfunction, which includes painful intercourse and the inability to become aroused or orgasm with sexual activity.
- Conditions that cause pain, fatigue, or reduced movement. Conditions such as arthritis, common among middle-aged people, can also cause or contribute to loss of libido.
- Use of certain medications. Medications such as antidepressants, amphetamines, hormonal drugs, and illicit drugs can diminish sexual functioning and cause or contribute to a loss of libido.
Loss Libido & Induced Menopause
Women who go through medical or surgical menopause often experience menopausal symptoms more suddenly and intensely than women going through natural menopause. Induced menopause can increase the likelihood of loss of libido.
- Hysterectomy. Hysterectomy can influence a woman's sexuality in different ways. Some women experience new sexual sensations after hysterectomy. In some cases, women may experience an increase in libido following hysterectomy, because they are now free from pain, uterine bleeding, and pregnancy worries. However, when the ovaries are removed or otherwise affected by hysterectomy, a woman may experience more intense menopause symptoms - including loss of libido - caused by hormonal disruptions.
In addition to physical causes, psychological issues can also cause or contribute to loss of libido in menopause. Keep reading to understand these causes of loss of libido.
Psychological causes
Research
One study found that anxiety was one of the biggest factors in decreased sex drive for women during menopause.
Psychological factors and the normal stresses of daily life can cause or contribute to loss of libido during menopause. Psychological causes of loss of libido can include:
- Stress
- Changes in self-esteem and body image
- Concerns about aging
- Feelings about sex outside the reproductive context
- Psychological disorders (e.g., mood swings, depression, or anxiety)
Factors relating to relationships, which sometimes have a psychological dimension, can also cause or aggravate loss of libido during menopause. Read on to learn more about these causes of loss of libido.
Relational causes

A woman's intimate, family, and social relationships can have a significant effect on how she feels sexually. For example, unresolved or past issues with a partner can cause or exacerbate loss of sexual desire during menopause. Major life changes can also cause a loss of libido. The most common relational factors causing or contributing to of loss of libido include:
- Changes in partner's physical health
- Changes in intimate relationship
- Availability of partner
- Lack of communication between partners
- Changing social role
- Family changes, such as children moving out
- Low sex drive in partner
Studies have shown that if a postmenopausal woman has a sexually-enthusiastic partner, her libido is typically maintained for many years following menopause.
While the causes of loss of libido are many and complex, women often find that lifestyle changes and natural remedies can do wonders to stimulate libido around the time of menopause. To learn more about these safe and effective treatments of loss of libido, read on to the next section.
Sources
- National Health Service UK. (2014). Sex after the menopause. Retrieved April 11, 2016, from http://www.nhs.uk/Livewell/women4060/Pages/sex-after-the-menopause.aspx
- Office on Women's Health. (2010). Menopause and sexuality. Retrieved April 11, 2016, from http://womenshealth.gov/menopause/menopause-sexuality/
- Sarell, P. (1999). Psychosexual effects of menopause: Role of androgens. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology, 180, 3S-II.
- Woods, N.F. , Mitchell, E.S. & Smith-Di Julio, K. (2010). Sexual Desire During the Menopausal Transition and Early Postmenopause: Observations from the Seattle Midlife Women's Health Study. Journal of Women's Health, 19(2), 209-218. doi: 10.1089/jwh.2009.1388
