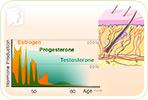
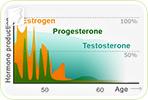
If you're experiencing postmenopausal hair loss, you are one of many women suffering from the same symptom. Although this type of hair loss usually begins in the early stages of perimenopause, its effects often are not noticeable until postmenopause.
Coping with Hair Loss and Thinning
Because the causes of hair loss are often hormonal, a major step you can take towards slowing or preventing it is to maintain your overall health. Below are a few recommendations to help prevent hair loss or promote the regrowth of hair.
Examine your medicine cabinet
Sometimes, the medication you are taking for other conditions can cause or accelerate hair loss as a side effect. Such medications include blood thinners, thyroid medication, and beta-blockers. If you think your medication may be behind your hair loss, talk to your physician before stopping, changing doses, or switching medication.
Try a new hairstyle
Instead of letting hair loss put a damper on your style, try out a new haircut that could work with it. Shorter styles give hair lift and volume, while a zigzag part can complement hair thinning on the top of the scalp. Coloring hair and adding layers on the top can also give hair more fullness.
Revise treatments and products
Chemical processes, such as bleaching and perming, can damage even healthy hair. Try rubbing natural oils, such as coconut or diluted rosemary oil, on the scalp reduce future hair loss.
Wash and dry with care
If you usually wash your hair every day, try cleaning it only every other day. Using a hairdryer afterwards can damage hair strands and increase breakage, so use a low-friction towel to blot dry hair when possible.
Try not to stress
High and prolonged stress levels can take a toll on your hair. In addition, the disturbing experience of hair loss can fuel additional stress. Some stress may be inevitable, but you can break the cycle by engaging in relaxing exercises, such as tai chi or yoga.
Watch your nutrient intake
Make sure you're getting plenty of protein, since this is the nutrient that is essential for your body to grow hair. You can get protein by eating chicken, eggs, and legumes. Iron and vitamin D are other important nutrients; a deficiency in them is related to hair loss. Iron is found in the protein-rich foods mentioned above, while vitamin D is made by the body when you spend time in sunlight.
Recommendation
Headbands, scarves, and hair wraps are becoming a popular way to mask hair loss, and they can help conceal the problem while other management methods are still taking effect. Click on the following link for more information on postmenopausal hair loss treatments.
Sources
- Dinh, Q.Q. & Sinclair, R. (2007). Female pattern hair loss: Current treatment concepts. Clinical Interventions in Aging, 2(2), 189-199. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2684510/
- Murata, K. et al. (2013). Promotion of hair growth by Rosmarinus officinalis leaf extract. Phytotherapy research, 27(2), 212-217. doi: 10.1002/ptr.4712
- National Institutes of Health. (2014). Female pattern baldness: MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. Retrieved October 20, 2015, from http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/001173.htm
- Park, S.Y. et al. (2013). Iron plays a certain role in patterned hair loss. Journal of Korean medical science, 28(6), 934-938. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.6.934
- Rasheed, H. et al. (2013). Serum ferritin and vitamin D in female hair loss: do they play a role? Skin pharmacology and physiology, 26(2), 101-107. doi: 10.1159/000346698
- Rele, A.S. & Mohile, R.B. (2003). Effect of mineral oil, sunflower oil, and coconut oil on prevention of hair damage. Journal of cosmetic science, 54(2), 175-192. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12715094