Diabetes is a lifelong condition in which the body's blood sugar levels are too high. Worldwide, 371 million people have diabetes, and that figure is expected to grow to 552 million by 2030. There are two types of diabetes - type 1 and type 2 - with different causes, symptoms, and treatment methods, but one symptom both types share is hair loss.
What's The Difference between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease diagnosed primarily in those under 40 - usually children and young adults - where the pancreas gland does not produce any insulin. Insulin is the hormone that controls blood glucose levels, and without it, glucose levels can become too high or too low, which damages the body's organs, blood vessels, and nerves, and if it goes without proper treatment, it can result in a coma or death. However, type 1 diabetes can be managed with insulin injections and close attention to blood sugar levels, although it cannot be completely cured.
Type 2 diabetes typically occurs later in life, when the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin to control glucose levels, or body cells become resistant to insulin. Unlike type 1, it can be triggered by obesity, when excess abdominal fat releases chemicals that disrupt the body's metabolic and cardiovascular systems. 90% of all diabetes cases are type 2, and the condition is usually managed - and sometimes reversed - with a healthy diet and tablets; insulin injections are normally unnecessary. Unlike type 1 diabetes, which cannot be prevented, type 2 diabetes can generally be prevented by maintaining a healthy weight and eating a healthy diet.
How Does Diabetes Cause Hair Loss?
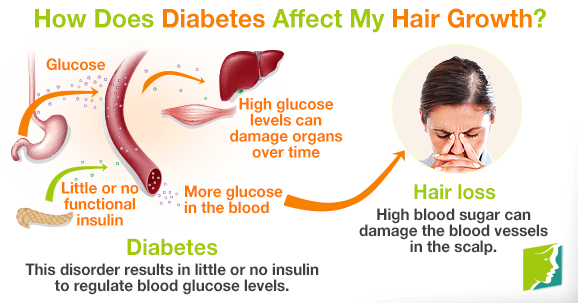
While researchers are unsure precisely how diabetes leads to hair loss, there are two likely causes.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease: abnormal functioning of the immune system causes it to produce white blood cells that attack the body's own tissues. Because hair loss occurs in many autoimmune disorders, it is thought that when white blood cells attack growing cells in the hair follicles, the follicle cells become small and hair production slows. This can cause hair from the scalp, eyelashes, eyebrows, and body hair to fall out, known as alopecia areata.
High blood sugar levels can also damage small blood vessels in the body over time. Especially in untreated type 2 diabetes, the scalp's blood vessels may get damaged, meaning less oxygen and nutrients reach the hair follicles. This can result in hair thinning and halt new hair production, so strands may not grow back once they fall out.
Will My Hair Grow Back?
Alopecia, the medical term for hair loss, is not a very well understood condition, so it is a difficult to make predictions about it. However, in most cases of alopecia, hair will grow back in a few months. However, in other cases, those who have alopecia experience hair loss and regrowth in phases.
What Treatments Are Available for Alopecia?
Although a lot of research and trials have been done and are ongoing to try to find a cure for alopecia and other forms of baldness, there is no one cure that works for all women that have alopecia. However, some medical treatments include:
Corticosteroids. These are injections or topical creams or ointments of steroids, helping treat small patches of baldness by suppressing the immune system in limited areas. The immune system is usually what is responsible for attacking hair follicles and causing hair loss.
Minoxidil lotion. This can be applied to the scalp and treat baldness in both men and women over several months of use, although it should not be used in anyone under 18.
There are many medicinal treatments available, but many do not work, and most have side effects, so it is important to talk to your doctor before making decisions about what hair loss treatment is right for you.
Many women who have experienced hair loss use wigs, scarves, and hats to create an appearance that makes them feel comfortable. It is also possible to use makeup and tattoos to fill in eyebrows.
Sources
- Gude, D. (2011). Hair - A Yardstick for Diabetes. International Journal of Trichology, 3(2), 131. doi: 10.4103/0974-7753.90852
- Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation. (2015). General Diabetes Facts. Retrieved August 4, 2015, from http://jdrf.org/about-jdrf/fact-sheets/general-diabetes-facts/
- National Health Service UK. (2015). Hair loss. Retrieved August 4, 2015, from http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Hair-loss/Pages/Introduction.aspx
- National Institutes of Health. (2014). Diabetes. Retrieved August 4, 2015, from http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/diabetes.html
- National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. (2015). Questions and Answers about Alopecia Areata. Retrieved August 4, 2015, from http://www.niams.nih.gov/Health_Info/Alopecia_Areata/#2